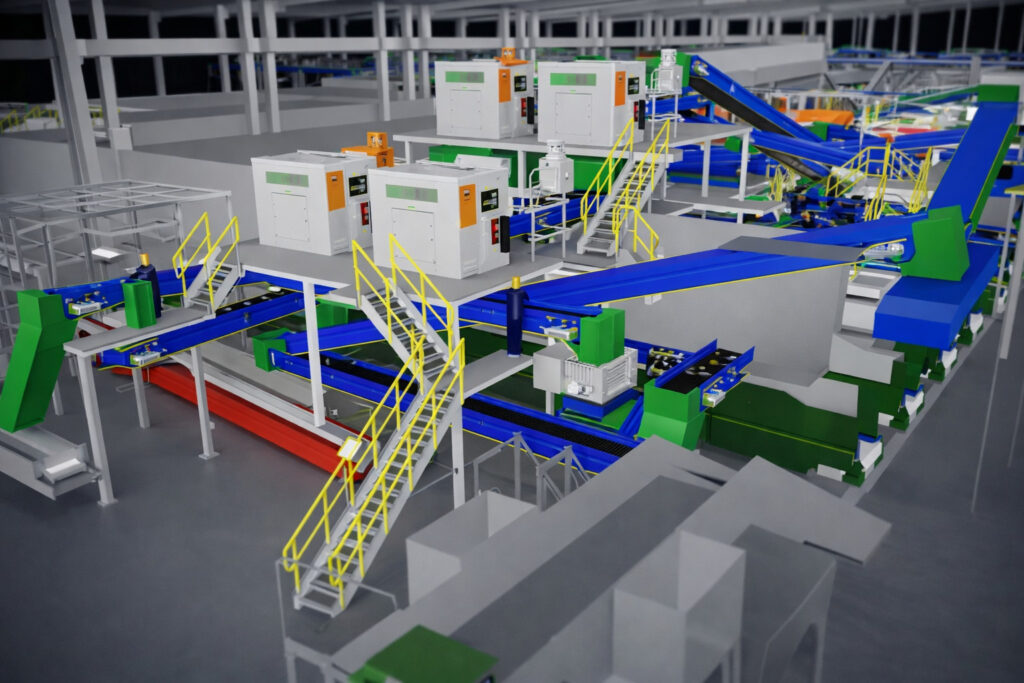
Serving the entire island of Tenerife, the Arico complex is the backbone of local MSW treatment. As with many island territories, operational constraints such as limited landfill capacity, high logistics costs and restricted access to downstream recycling markets place increased pressure on treatment facilities to maximise recovery efficiency and stabilise output quality. Within this context, advanced sorting technology is a critical enabler.
A technology-led upgrade of the plastics line
PICVISA’s contribution to the Arico project is concentrated on the plastics fraction of the MSW treatment line, where a multi-layered configuration of optical sorters, robotic picking and vision systems has been deployed.
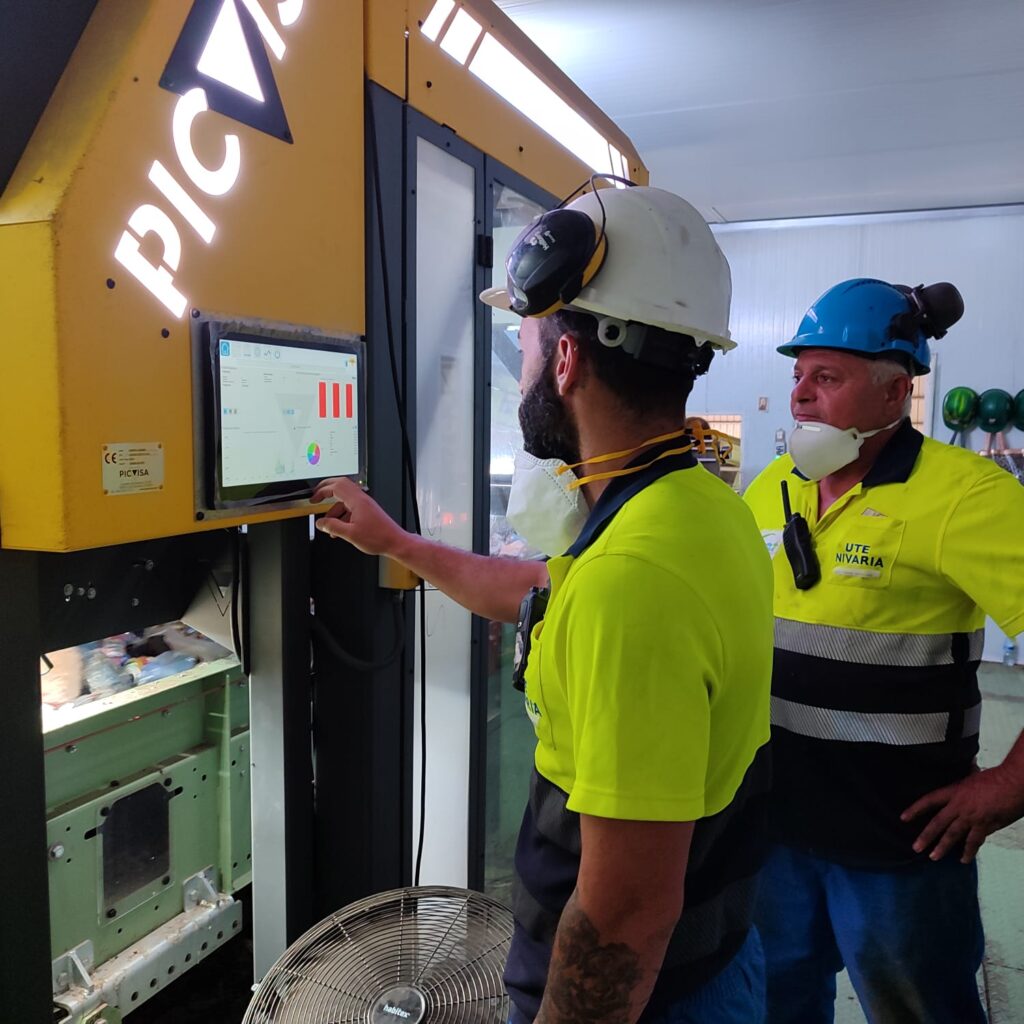
At the core of the installation are seven ECOPACK optical sorting units, supplied by PICVISA and currently installed, commissioned and approved for operation. These systems form the backbone of plastics separation, processing mixed and variable MSW streams under real production conditions.
The ECOPACK units use optical sensing technologies combined with advanced classification algorithms to identify and separate target plastic fractions. Designed to operate under the fluctuating feedstock conditions typical of residual MSW, the systems aim to stabilise throughput while improving recovery rates and consistency of output.
According to project stakeholders, this is the first time such a high number of ECOPACK units have been deployed within a single URBASER facility, positioning the Arico complex as a reference installation within the operator’s portfolio.
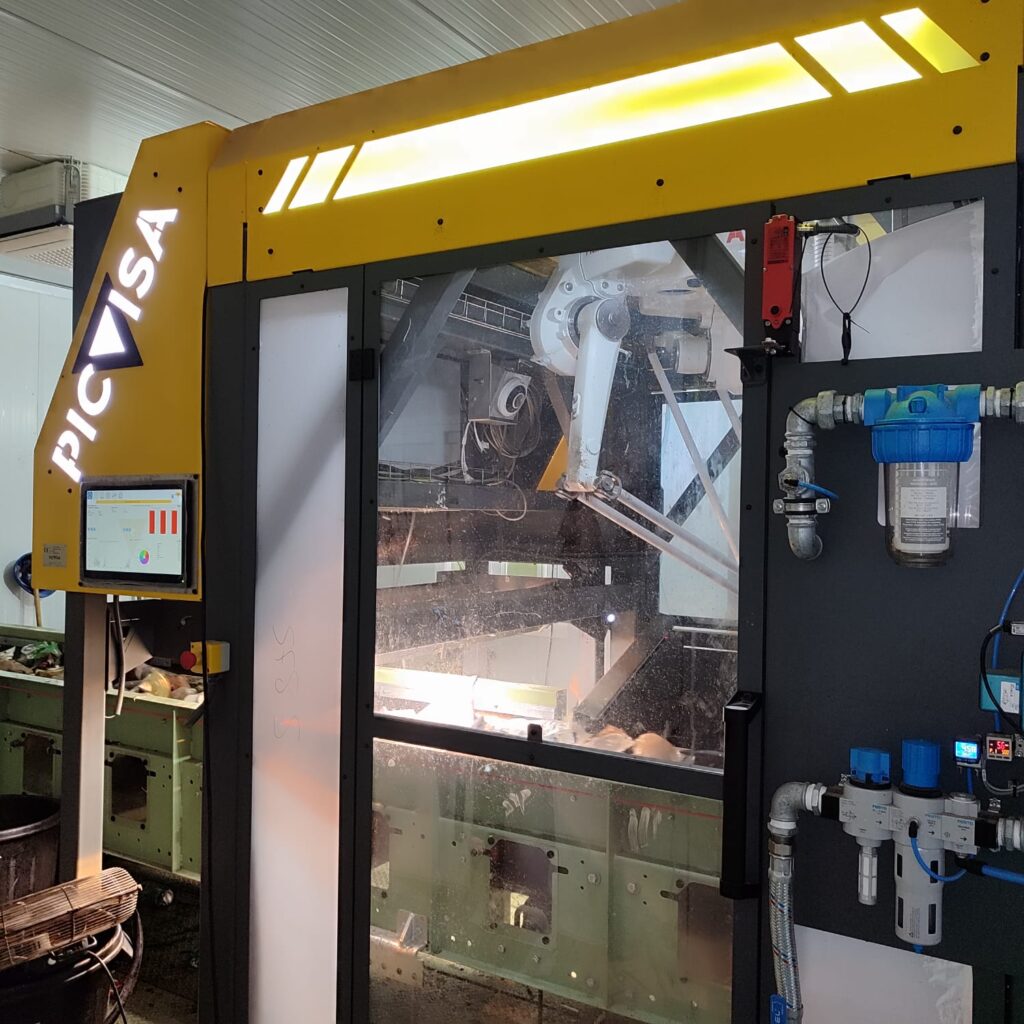

Robotic recovery at the rejection stage
To complement the optical sorting stage, PICVISA has supplied an ECOPICK robotic picker, installed in the manual sorting cabin on the reject conveyor.
Unlike conventional robotic installations focused on positive picking, the ECOPICK system at Arico operates on the rejection stream. Its role is to recover valuable materials—primarily PET, HDPE and CBA —that would otherwise be lost at the final stages of the process.
Equipped with a suction-based gripping system, the robot is designed to handle irregular shapes and variable material presentation, which are common characteristics of MSW-derived rejects. By targeting missed valuables rather than primary fractions, the system adds a flexible recovery layer without increasing manual sorting requirements.
This configuration reflects a growing trend in advanced MSW plants, where robotics are increasingly used to enhance overall yield rather than replace core sorting equipment.
Vision-based control of output fractions
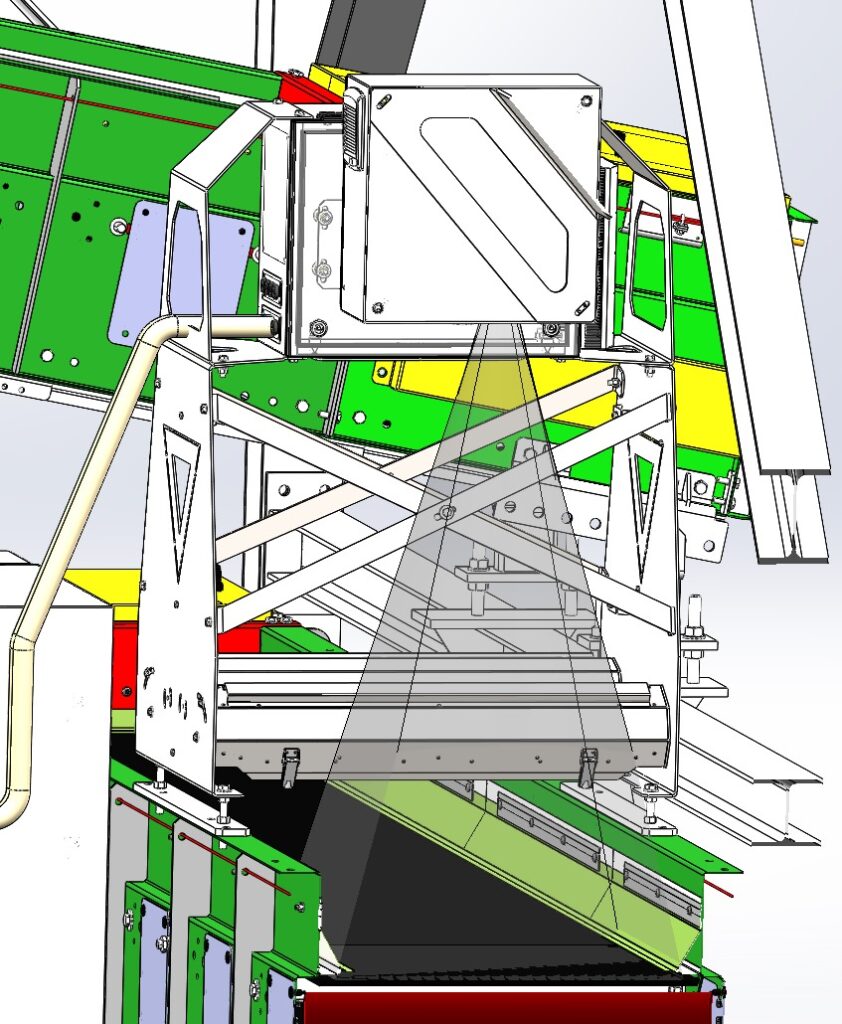
Further downstream, PICVISA has installed ECOFLOW units combined with ECOEYE vision systems on two key output streams.
One configuration is installed on the HDPE output belt, where it continuously analyses the material flow and uploads process data to the cloud. Through PICVISA’s DATA+ platform, this information can be used to monitor plant performance, evaluate material flows and support data-driven operational decisions over time. A second system targets the aluminium fraction, contributing to improved separation efficiency and reduced cross-contamination.
These vision-based systems act as fine-tuning elements within the overall process, allowing greater control over final material quality. Their integration illustrates PICVISA’s approach of combining multiple technologies—optical sorting, robotics and computer vision—within a single process layout.
Equipment supply within a multi-partner project
PICVISA’s scope at Arico is limited to the supply of sorting equipment. Mechanical installation, electrical works and overall plant integration are managed by other project partners.
Despite this separation of responsibilities, the project has been structured to allow close coordination between the technology supplier and the plant operator. This coordination is essential in complex MBT upgrades, where the performance of individual systems depends heavily on their interaction with upstream and downstream processes.
From installation to long-term optimisation
A defining feature of the Arico project is that it extends beyond equipment delivery. The contract includes full sensorisation and a two-year technology partnership between PICVISA and URBASER.
This framework enables continuous monitoring of system performance and provides the basis for ongoing optimisation driven by operational data. Detection models, sorting parameters and process logic can be adjusted over time to reflect the specific characteristics of Tenerife’s MSW stream.
Such long-term collaboration reflects a broader shift in the recycling sector, where technology providers increasingly support post-commissioning performance rather than limiting their role to initial installation and acceptance testing.
Integration within a wider modernisation programme
The plastics sorting upgrade forms part of a broader transformation of the Arico Environmental Complex. Supported by public funding under Spain’s Recovery, Transformation and Resilience Plan, the overall project includes:
- New automation per MSW treatment line
- Additional optical sorting systems
- Ballistic separators
- Ferrous and non-ferrous metal separation
- Advanced aspiration systems for light materials
Together, these measures aim to increase recovery efficiency, reduce landfill dependency and align the facility with current and future regulatory requirements.
In parallel, the site has also implemented an advanced leachate treatment system, combining reverse osmosis, evaporation and solidification technologies. The installation processes up to 300 m³ of leachate per day, generating more than 250 m³ of reusable industrial water for internal use, contributing to water self-sufficiency and reduced environmental impact.
Glass refining as a complementary development
Looking ahead, PICVISA is also involved in a separate project at the Arico site: the installation of an ECOGLASS optical glass refining line for MSW -derived glass. The new line is currently under construction in an area adjacent to the plastics treatment zone.
Once operational, the glass refining system is expected to further enhance material recovery and output quality, reinforcing the site’s evolution from a conventional MBT facility toward a multi-material resource recovery hub.
A reference case for advanced MSW sorting
The Arico project demonstrates how advanced optical and robotic sorting technologies can be integrated into large-scale MSW treatment facilities to address the specific challenges of island waste management.
For URBASER, the project strengthens its position as an operator of technologically advanced treatment plants. For PICVISA, it represents a reference installation, combining multiple optical sorters, robotic recovery and vision-based quality control within a single MSW plastics line.
More broadly, the case highlights an industry-wide shift toward data-driven, adaptable sorting systems supported by long-term technology partnerships—an approach increasingly seen as essential for achieving stable performance and higher recovery rates in complex waste streams.