Battery Recycling
Experts for Battery Recycling

Ankit Kalola
Fornnax Technology Pvt. LtdMr. Ankit Kalola serves as the Global Head – Sales at Fornnax Technology Pvt. Ltd, where he has played a pivotal role in shaping the company’s sales strategy and global footprint. A seasoned expert in shredding systems and end-to-end recycling solutions, he excels in building client-centric approaches, driving market penetration, and aligning technical solutions with customer needs. His strategic direction has significantly contributed to Fornnax’s success across diverse industries and geographies. Mr. Kalola’s leadership continues to fuel growth, innovation, and long-term partnerships worldwide. For further information or to connect with Mr. Kalola, please reach out at +91-9033077711 or email: info@fornnax.com.

Tom Jansen
TOMRA RecyclingAfter studying Chemical Engineering at the Technical University of Eindhoven, the Netherlands, Tom started working as Sales Engineer at Innov-X Systems. He initially focused on selling handheld XRF equipment in the Benelux, while gradually extending the geographical territory over the years. From 2007 he was heavily involved in the pioneering of automated XRF sensor technology, bringing this new technology to the metal scrap market worldwide. Tom joined TOMRA Sorting (then Titech GmbH) in 2011 as Sales Manager responsible for the Metal Recycling market in the Netherlands and Belgium. Since then, in his role as Segment Champion for the ELV shredder segment, he has also supported the metal recycling market in the Middle East region, Italy, Greece and projects in several other countries.
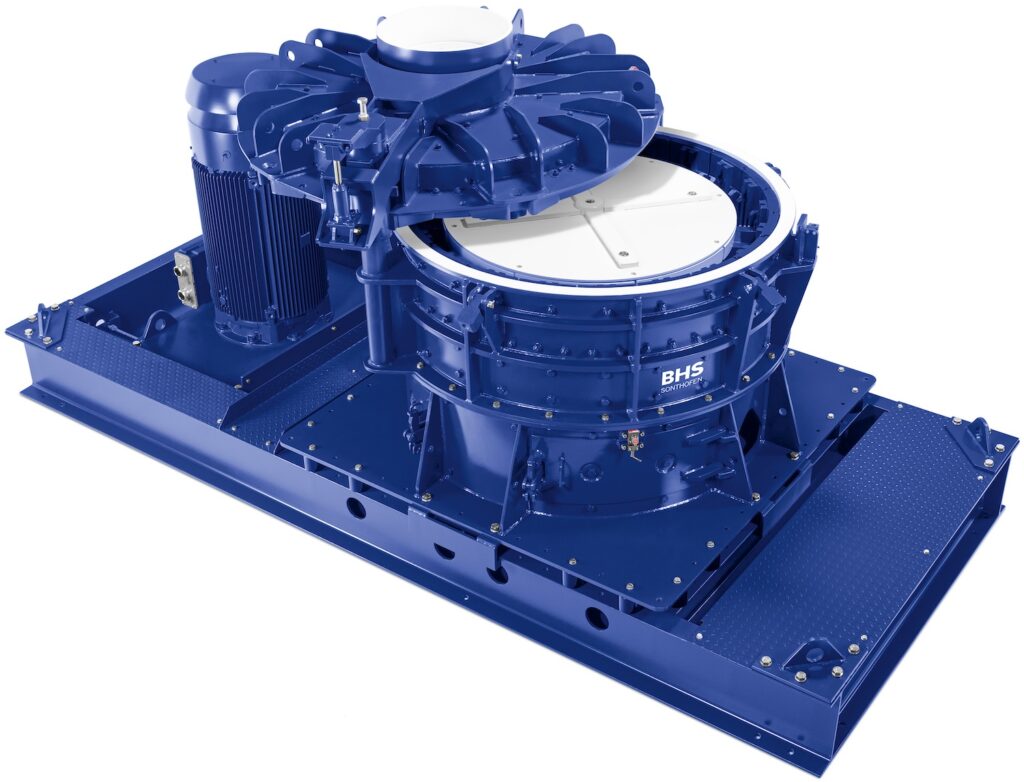
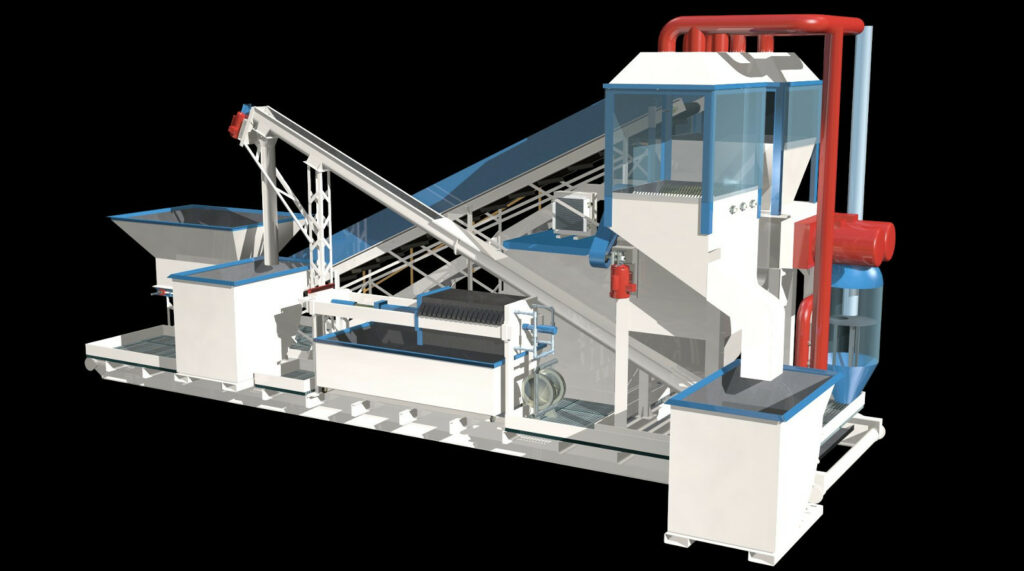
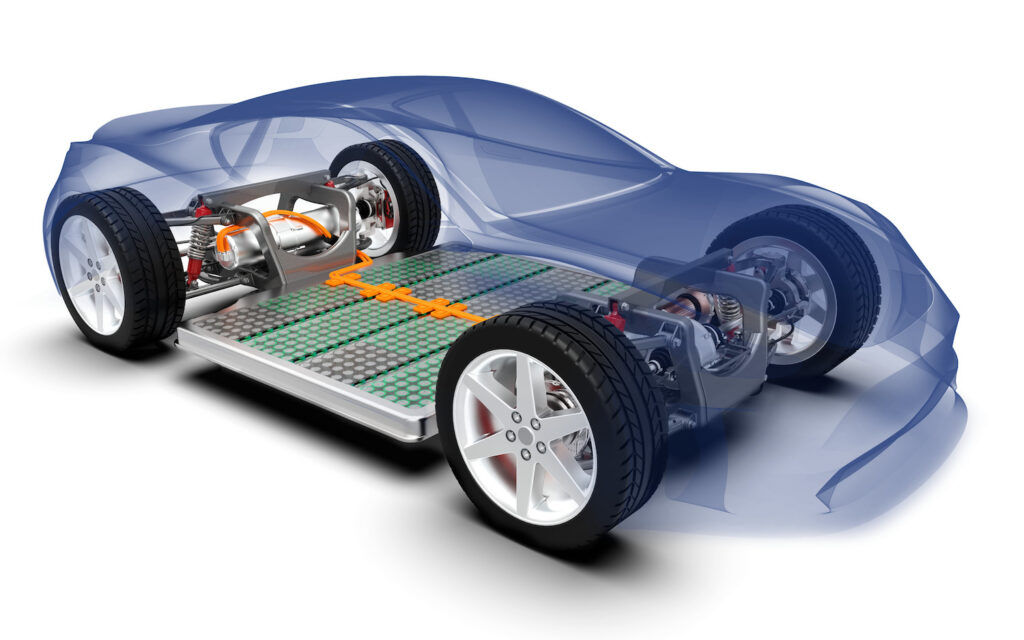
Battery recycling is the process of safely collecting and reprocessing used batteries to recover valuable materials and prevent environmental harm. Batteries contain metals like lead, lithium, nickel, and cobalt, which are non-renewable resources and can be toxic if not managed properly. Recycling helps extract these materials for reuse, reducing the need for new mining and minimizing the risk of soil and water contamination.