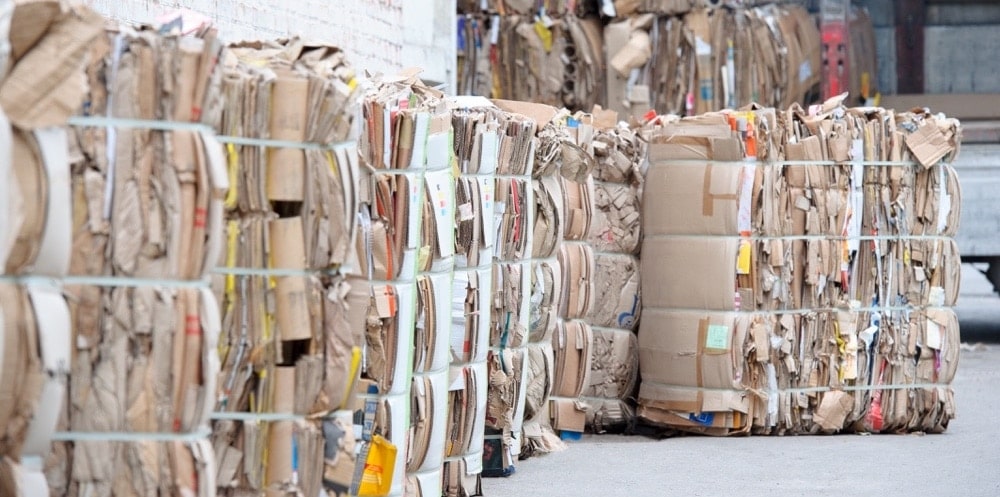
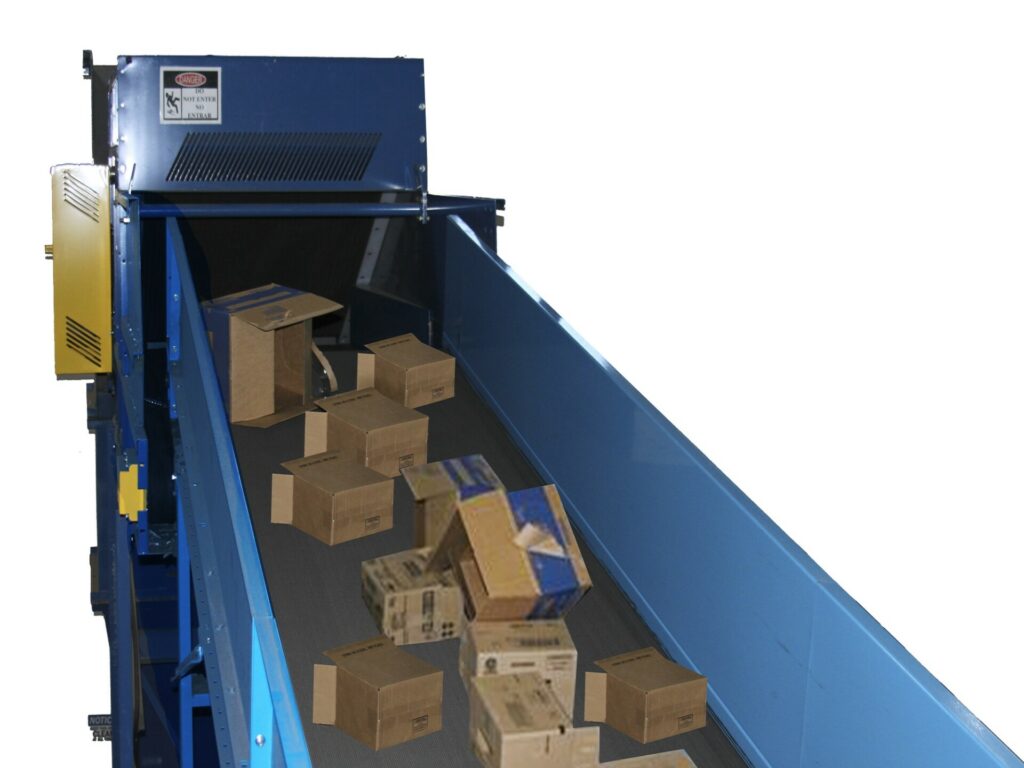
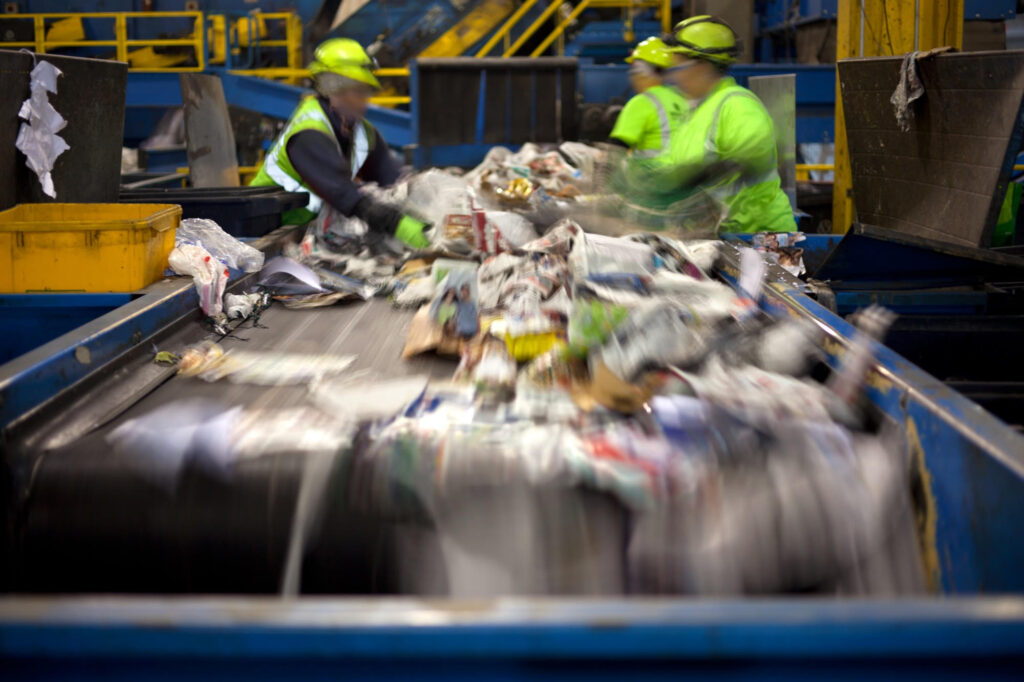
Collection: Recyclers and businesses collect the waste cardboard in cardboard recycling containers, and the separated cardboard is transported to a cardboard recycling plant.
Sorting: Once the waste cardboard reaches the cardboard recycling center, it needs sorting. This sorting is done based on the type of cardboard, with the two popular types being boxboard and corrugated board.
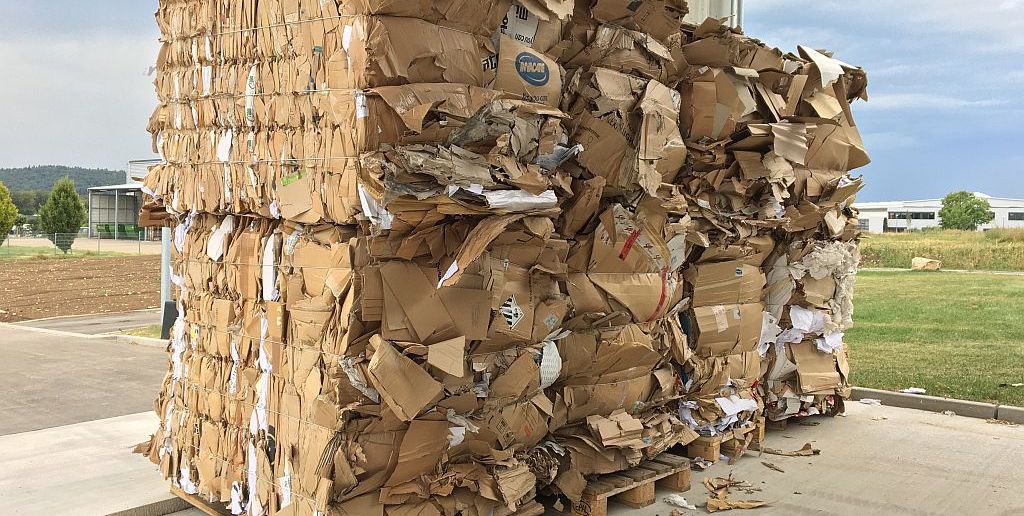
After the sorting is done, the cardboard is then baled. For this purpose, machines such as cardboard balers are used to ensure that the cardboard is compressed into compact bales that are easy to handle.
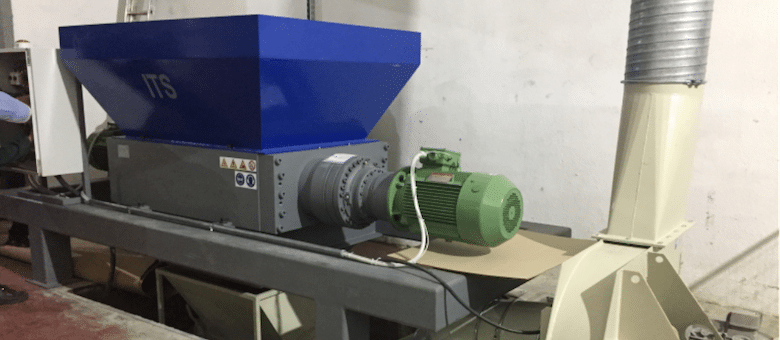
Shredding and pulping: The next step is shredding, and then pulping follows. Shredding is done to break down the cardboard paper fibers into minute pieces. When the material is shredded, it is soaked in water. Cardboard recycling centers will also use chemicals that hasten the pulping process. The pulped material is then blended with new pulp, generally from wood chips that ultimately help the resulting substance to solidify and become firmer.
Filtering, conterminal removal, and de-inking: The pulped material is taken through a comprehensive filtering process to get rid of all the foreign materials present and impurities such as tape, strings, or glue. The pulp further goes into a chamber where contaminants like plastics and metals staples are removed through a centrifuge-like process.
The following process is de-inking; any color that the pulp has will also be removed using a floatation device that employs de-colorization chemicals.
Finishing for reuse: At this stage, we are looking at a pulp that is ready to be given the desired shape. Virgin paper materials are added, followed by drying. Drying is done either on a conveyor belt or table. As it dries, the material is fed through a machine that squeezes excess water and helps the fibers form a solid sheet called a linerboard. The linerboards are glued together, layer by layer, to make a new piece of cardboard.