What precious metals are found in electronic wastes?
Precious materials such as gold, silver, copper, platinum, and palladium are used in the process of electronic devices. So, the interest in the recycle of precious metals from e-waste continues to increase day by day.
Is E-Waste Recycling profitable investment?
Even though producing and selling technology is a very profitable investment, all those products are open to recycling and the recovery of precious metals used in the production of electronic devices is possible with the application of the right process. But the issue is, what is the right process and how can you make an e-waste plant. In this essay, I will give you some information about e-waste and e-waste plantations.
Importance of E-Waste Recycling
Many precious metals are used in the manufacture of electronic devices. We can recover precious metals such as gold, silver, copper and palladium in all electronic wastes and scrubs. Then what is e-waste? We can include e-waste from our mobile phones to modems, computers, televisions, etc. all of expired, broken electronic devices can be used in e-waste recycling. There is no doubt that recycling all of those e-wastes is a profitable investment, such as the recycling of precious metals, but at the same time, recycling of e-waste is extremely beneficial investments in order to protect our nature. All of expired electronical devices has harmful toxic residues. These electronic wastes often contain toxic chemicals and hazardous materials. This can have extremely harmful effects on wildlife, human health, and the environment. If we keep those in thrash pile, e-waste will damage to our nature. Therefore, recycling of e-waste is an environmentally investment as well as a profitable investment. Despite technological advances and research, only a small part of e-waste is taken for recycling. How accurate can it be to define all these electronic wastes as garbage among so many treasures?
How is E-Waste Recycling Process?
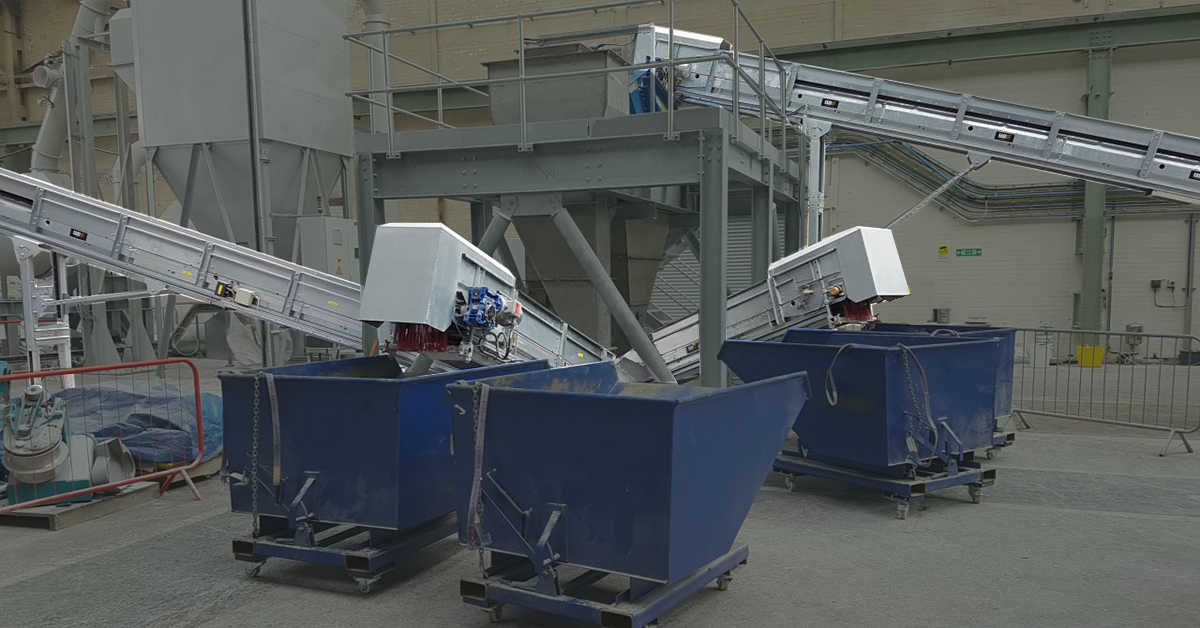
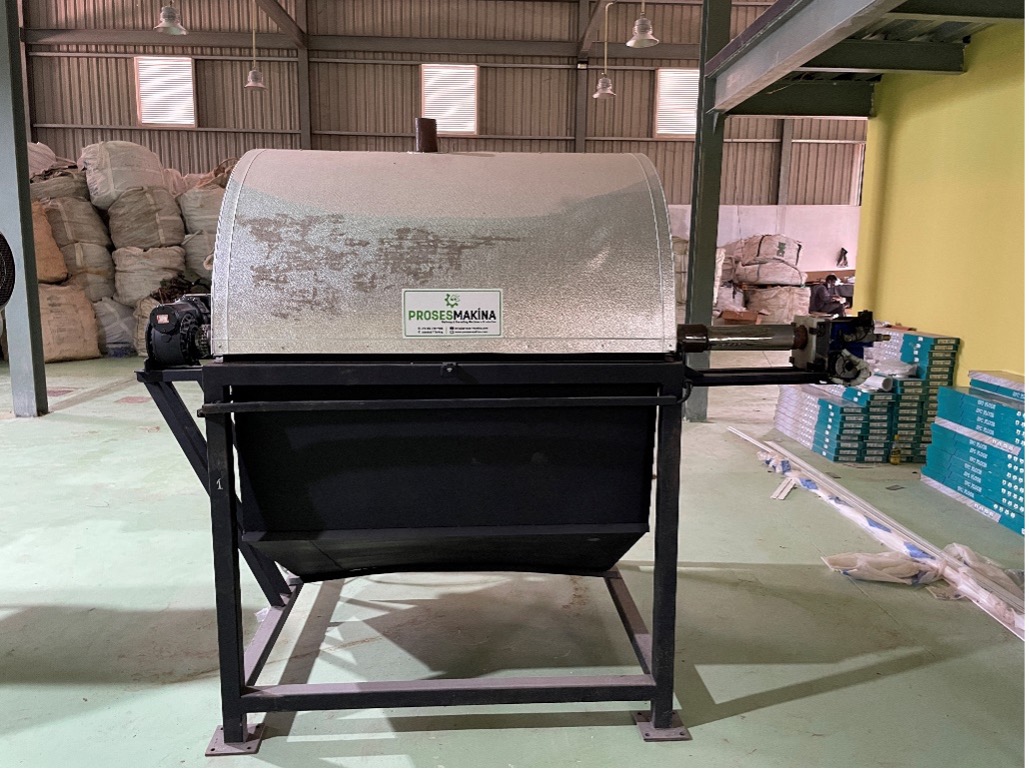
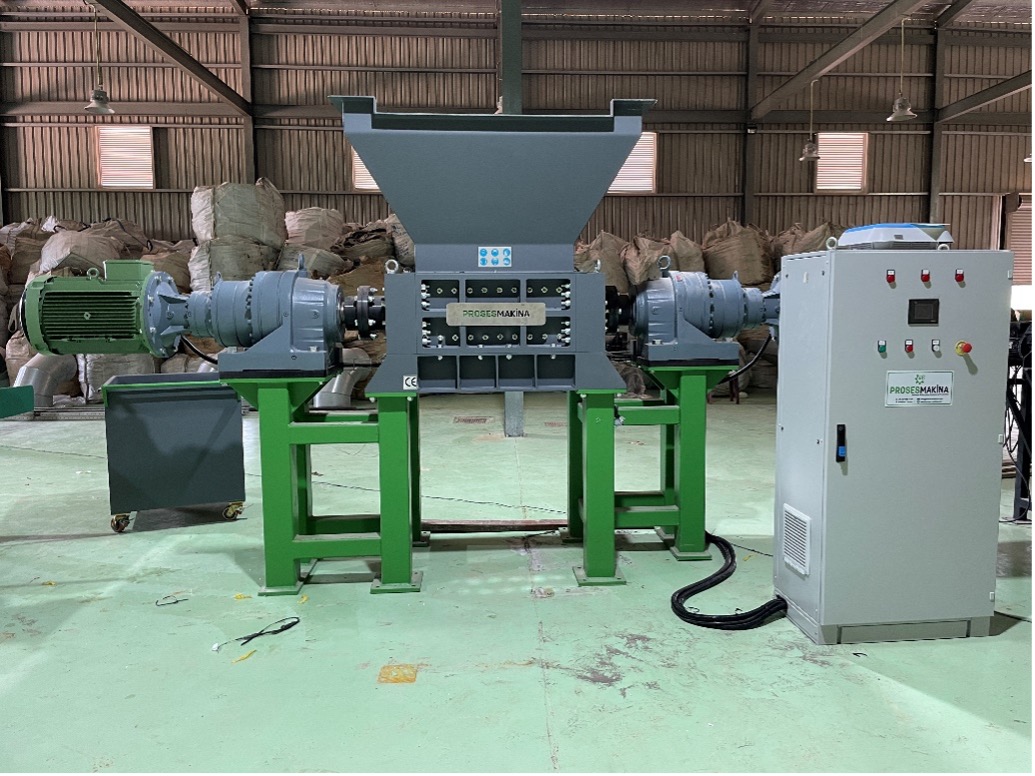
The electronic waste recycling process is basically a multi-stage process consisting of chemical and physical steps. Although the process is generally the same for electronic wastes, if you are going to work with a specific product group or depending on your capacity, our solution may be different for you. Please contact Proses Makina Co. for detailed information. The physical process is the process of bringing the parts that are input to the system to a sufficient size physically. The electronic wastes we have for recycling were soldered and held together during production. We have to separate some worthless materials and iron from our electronic wastes. Proses Makina’s component separator is working in specific working temperature for separate those materials from our e-waste. The pieces coming out of the separator are then shredded and converted into a much smaller granular structure, increasing the surface area of the materials. You can see our component separator and shredder unit below.


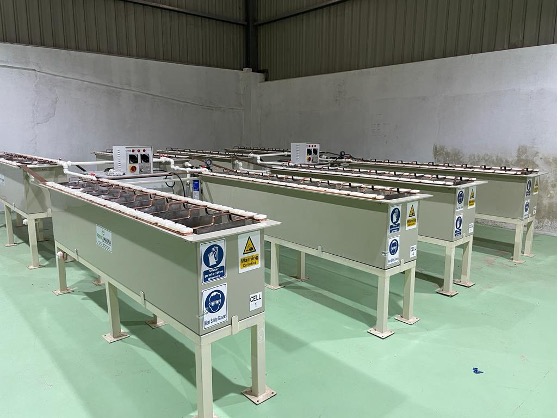
The materials coming out of shredder have some dirt and grime. We need to wash those on the shaking table. If we do not wash our materials, our efficiency will decrease. The table works principal separation from density difference. When the washing process has finished, we have to move the next step. Our parts have to be dried before entering the rotary furnace. The dryers save time and work. The parts coming out of the dryer are now ready to enter the oven for melting process.
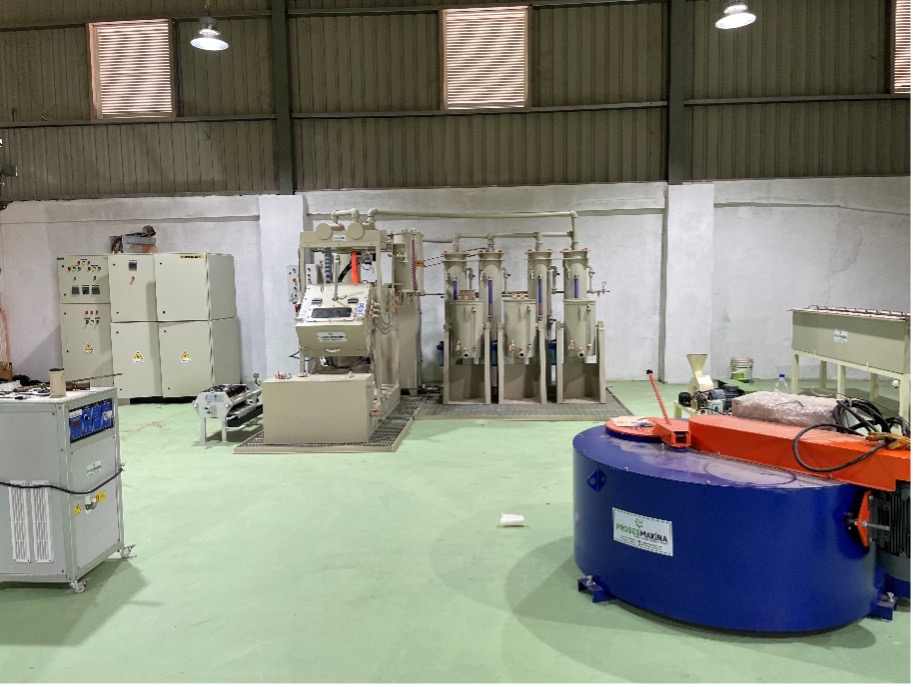
Melting unit aim to remove lead and tin from precious metals. System designed for the recovery and refining of precious metals.
How is E-Waste Recycling Chemical Process?
Melted products goes to the mold casting unit. Mold casting unit designed for producing anodes for electrolysis unit. The mold casting unit has its own pre-heating system. The chemical process begins after the casting process is finished. Our chemical process consists of electrolysis, refining and neutralization units. The first step is chemical process is electrolysis after the mold casting. We can recover high purity copper from our electrolysis unit. Precious metals and copper are separated into the electrolysis unit. We can collect the copper onto the cathode and the precious metals are during into the anode sludge and then the process continues with refining for the recovery of precious metals. We can obtain precious metals such as high purity gold, silver, palladium, and platinum. Every precious metal has separate chemical processes. Technical training is provided by Proses Makina. We have wastewater after all chemical process and wastewater is neutralized after the chemical refining and electrolysis processes.


Proses Makina is a qualified company for planting e-wastes and applying the production of electronic waste facilities with its expert engineer team and advanced machinery. Proses Makina, with its experienced and expert staff in the field of e-Waste, with its many facilities that it has established in Iran, India, Sri Lanka, Vietnam, Pakistan, Egypt, Portugal, Spain, America-Virginia and currently working in different parts of the world. Contact to us to get detailed information about precious metal recycling from electronic waste and to be your solution partner. Proses Makina Co. has established in Istanbul, Turkey.