In catalytic converters connected to the exhaust outlet pipe of cars, the platinum group metals convert carbon monoxide gas (CO), hydrocarbons (HC) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) released into the air into less harmful carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor. Catalytic converters contain platinum, palladium and rhodium precious metals from platinum group metals as catalysts.
It provides the breakdown of platinum and palladium hydrocarbons into water vapor and carbon dioxide. Rhodium converts nitrogen oxides and carbon monoxide into nitrogen and carbon dioxide.
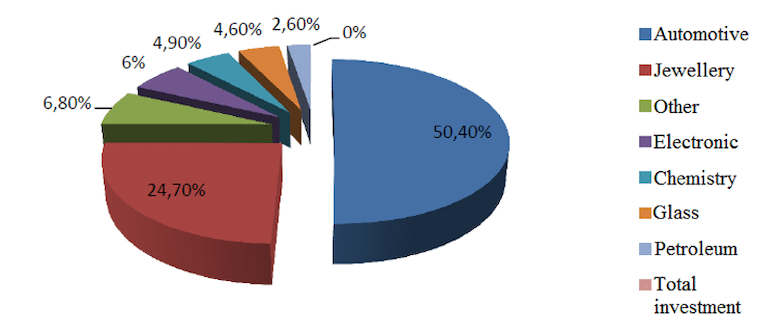
Use of % platinum group metal by sectors in 2006
In the figure, as seen in the data in 2006, more than 50% of the use of platinum group metals in the world is in the automotive sector. With the ever-increasing world vehicle stock, platinum group metal usage is more common today. In addition to this, the increase in the number of scrap vehicles and the fact that each scrap car included a catalytic converter brought along recycling and recovery processes.
The fact that the catalytic converters contain precious metals also enabled them to have an economic value. Considering the sum of precious metals used in the catalytic converters in scrapped vehicles since 1975, this amount is considerably higher. It needs to be recycled both environmentally, commercially and economically.
The amount of precious metal that can be obtained by processing approximately 360 kg of ore and rock from nature can be obtained by recycling one catalytic converter, which weighs about 1.5 kg. Recycling costs are lower than ore production costs and environmental awareness can be increased. Because it is possible to produce more by polluting less and consuming less.
What is the value of precious metals?
Catalytic converters have economic value as they contain precious metals. This is the main reason why they are sold as the most expensive scrap. Because it contains rhodium, palladium and platinum, which are among the most precious metals. They can be converted into more cash when Pt, Pd, Rh are recovered from the scrap catalytic converter.
How much is a gram of Platinum worth?
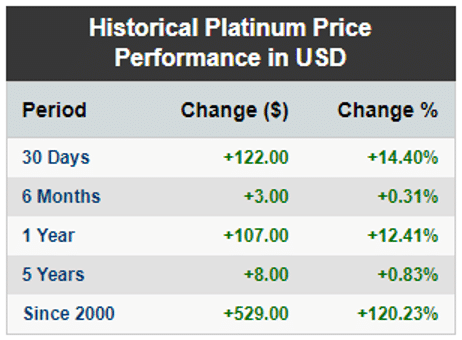
The worth of Platinum metal is increasing with time as its shown on the table. It’s economic value never decreased as seen in the table last 20 years. So that’s meaning Platinum’s value is getting more important every day.
Nowadays, the platinum price per gram is around $31.
How much is a gram of Palladium worth?
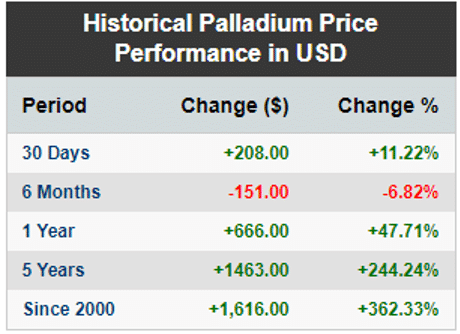
Considering the variability of the palladium value, although there was a decrease for a period, it did not cause a serious decrease in general. It is still valuable and its economic value continues to increase. Nowadays, the palladium price per gram is around $72.
How much is a gram of Rhodium worth?
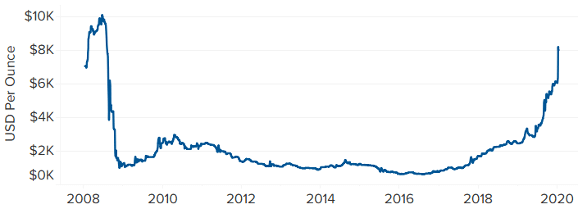
Looking at the change in the value of rhodium in the last 10 years, although it has remained stable most of the time, it has increased significantly in the last two years. Nowadays, the rhodium price per gram is around $287.
- Although the quantities vary by model, on average, only one standard catalytic converter contains about 3-7 grams of platinum, 2-7 grams of palladium, 1-2 grams rhodium. That provides serious gains when tons of scrap catalytic converters are recovered.
As Proses Makina Company, we provide you all precious metals in the scrap catalytic converter recovery for economic gain with our high efficiency, last technology systems.
Catalytic Converter Recycling Machines
- Decanning Unit; First, the catalytic converter is separated honeycomb from the exhaust.
- Milling Unit: The sample from the decanning unit is brought to the desired size. Thus, the surface area is increased and it is ready to reach high chemical efficiency.
- Vacuum Transfer Unit: It is added to the process according to the customer’s demand. The ground sample is transferred to the desired place by vacuum transfer.
- Double Conic Mixer: It is added to the process according to the customer’s request. It provides a homogeneous mixture of 2 or more materials of low, medium or high quality.
- Roasting Unit: At this stage, the sample is cleaned from high-temperature impurities before chemical treatment.
- Leaching Unit: We need to dissolve in leaching solution in order to reduce the amount and get only precious metals in high purity.
- Refining Unit: At this stage, chemical processes such as Pt, Pd and Rh, which we have taken into Leach solution, are applied separately. Each one is recovered in high purity.
- Waste Water Treatment Unit: It’s consists of neutralization and an Activated Carbon unit. Waste sludge from the chemical unit is made compatible with environmental laws.
It guarantees to recover at least 90% purity rhodium with 99.95% purity platinum and palladium.

























